In the world of visual marketing and corporate identity, flags are no longer just pieces of cloth fluttering above buildings; they have transformed into powerful communication tools that reflect the prestige of nations, the professionalism of companies, and the appeal of events. The industry has witnessed a radical transformation in recent years, moving from traditional methods relying on sewing and hand embroidery to an era of speed and digital precision.
In this extensive article, we will dive deep into flag printing technologies, and analyze the methods that have made it possible to print millions of colors with extreme precision on fabrics that withstand the harshest climatic conditions.
The Evolution of Flag Industry: From Craft to Technology

To understand the current reality, we must realize that flag printing technologies were not always this easy. Anciently, producing a complex flag required cutting colored pieces of cloth and sewing them together, making the production cost exorbitant and the weight heavy, not to mention the impossibility of executing complex color gradients or photographs.
Today, thanks to technological advancement, we can print a flag tens of meters wide with vivid colors that penetrate the fabric to appear on both sides with almost equal quality. This development has not only served the aesthetic aspect but also enhanced the lifespan of the flag and its ability to resist UV rays and strong winds.
Most Common Types of Flag Printing Technologies

The methods used in producing flags vary based on the purpose of use, the required quantity, and the type of fabric. Below is a breakdown of the most prominent of these technologies:
1. Dye Sublimation Printing
This technique is considered the “Gold Standard” in the modern flag industry. Its chemical concept relies on converting ink from a solid state directly to a gaseous state without passing through the liquid state, under the influence of high heat and pressure.
When the ink turns into gas, the pores of the polyester fibers (the primary material for flags) open up, allowing the gas to enter and bond with the fabric molecules. When the fabric cools, the pores close, and the ink becomes an integral part of the fabric, not just a layer on top of it.
Advantages of this technology:
-
Color penetration of 90-95% to the reverse side (very important for flags).
-
Colors do not fade easily or peel because they are embedded in the thread.
-
The fabric texture remains soft and does not stiffen.
2. Direct-to-Fabric Digital Printing
This method is one of the fastest-developing flag printing technologies. Giant printers (which can reach up to 5 meters in width) work by jetting ink directly onto the fabric roll. The fabric is then passed through special heaters (an oven) to fix the color.
This technology is often used for temporary advertising flags or large quantities requiring speed in execution, and it is excellent for designs containing very fine details and photographs.
3. Screen Printing
Although it is an old technique, it still holds an important place, especially in massive orders (thousands of flags with the same design). It relies on making a “cliché” or screen for each color in the design.
Technical Comparison Between Printing Methods
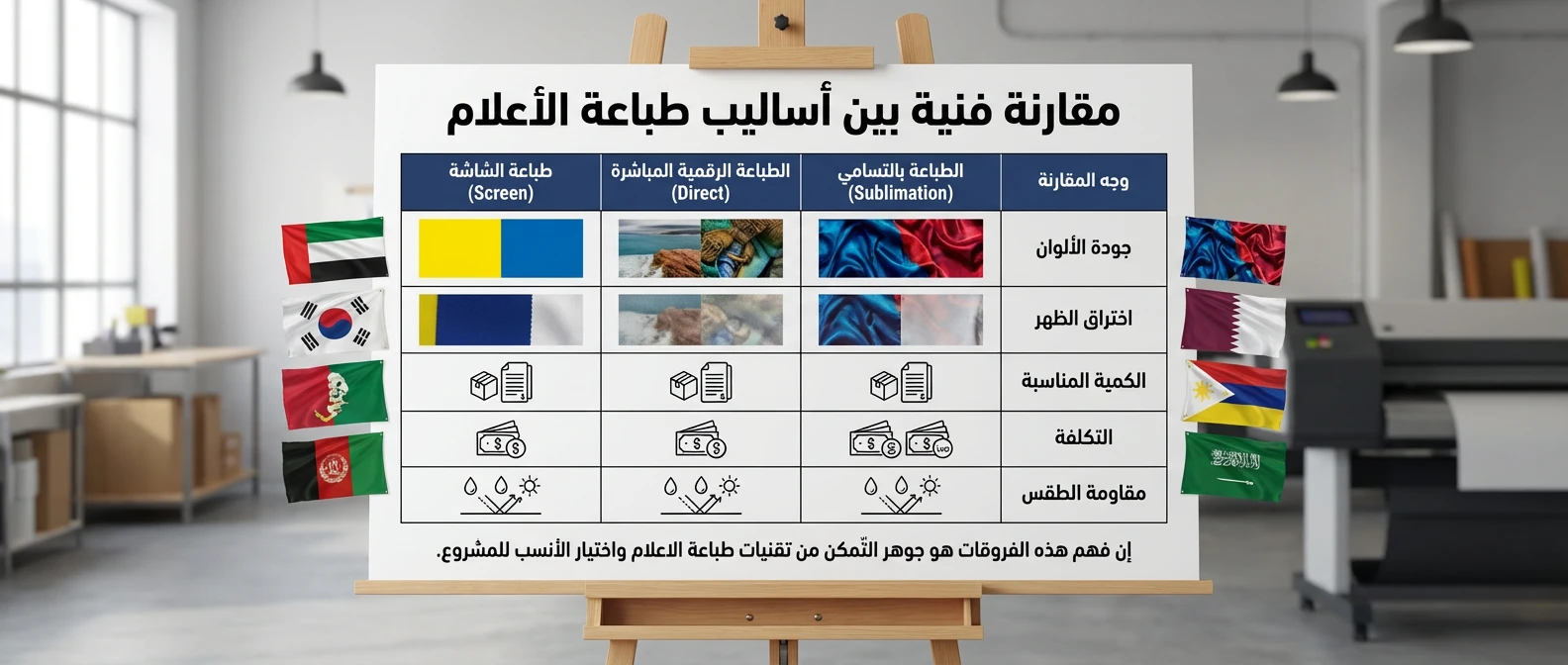
To clarify the fundamental differences for purchasing managers and print shop owners, we have prepared the following table comparing the most prominent methods used:
| Aspect | Sublimation | Direct Digital | Screen Printing |
| Color Quality | Excellent, vivid, and very deep | Very good, high detail accuracy | Solid and strong colors, but gradients are difficult |
| Back Penetration | Excellent penetration (image shows on back) | Good (depends on ink density) | Excellent (full ink penetration) |
| Suitable Quantity | From one piece to medium quantities | Small to medium quantities | Very large quantities only |
| Cost | Medium | Relatively high | Very low in large quantities |
| Weather Resistance | Very high (water and sun resistant) | Medium to high | Very high |
Understanding these differences is the essence of mastering flag printing technologies and choosing the most suitable one for the project.
Materials and Inks: The Backbone of Quality
The process is incomplete without discussing materials. Flags require a special type of fabric and ink to withstand constant wind fluttering and scorching sunlight.
First: Fabrics Used
-
Knitted Polyester: The most common, featuring pores that allow air to pass through, reducing wind resistance and prolonging the life of the flag and the flagpole.
-
Woven Polyester: Heavier and more durable, used for marine flags and in very windy areas, but harder to print on.
-
Satin: Used for indoor flags, office flags, and protocols due to its attractive sheen.
Second: Inks and Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology has entered the development of special inks used in flag printing technologies, where these inks feature ultra-small particles capable of deep integration with fibers, added with UV inhibitors to prevent color fading quickly in hot regions like the Gulf countries.
Criteria for Choosing the Right Technology for Your Project
When you decide to order flag printing, whether for a company or a national event, there is a checklist to consider to ensure the best result. Your wrong choice of technology might lead to a flag that tears after a week or whose colors fade.
The following table illustrates when to use each technology based on need:
| Flag Purpose | Suggested Technology | Reason |
| National Flag (Official) | Sublimation or Screen | To obtain accurate “Pantone” colors and long life. |
| Promotional Flag for One-Day Event | Direct Digital Printing | Lower cost and higher speed. |
| Small Flags (Handheld) | Offset or Digital | Precision in small details and low cost. |
| Beach Flags | Sublimation | To ensure the logo is seen clearly from both sides. |
Note that precision in choosing flag printing technologies saves the budget and ensures product sustainability.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Solutions in Flag Printing
The world is going green, and the printing industry is no exception. Traditional printing faced criticism for using large amounts of water and chemical waste.
Recently, strong trends towards “Green Printing” have emerged. The latest flag printing technologies now rely on water-based inks free of harmful solvents. Dye sublimation is also considered relatively eco-friendly because it does not consume water in the washing process as happens in traditional dyeing, nor does it produce polluted wastewater.
Furthermore, factories have started using Recycled Polyester fabrics manufactured from plastic bottles (PET), closing the sustainability loop completely.
Challenges Facing Outdoor Flag Printing
Despite immense progress, there are still physical challenges to overcome. The flag is the only printed matter exposed to “mechanical stress” (fluttering and constant movement).
- Bleed-through Issue: The biggest challenge in flag printing technologies is making the image on the reverse side as strong as the front side. In standard digital printing, the back side may appear 50% faded, making the flag look “cheap.” The solution lies in using chemically treated fabrics to increase absorption, and high heat pressure to push ink through fibers.
- Color Matching: Screen colors (RGB) differ from print colors (CMYK). In flag printing, it is more complex because the fabric absorbs light and does not reflect it like paper. Therefore, advanced color management software (RIP Software) is required to adjust color curves and ensure that the red in the company logo is the same red printed on the fabric.
The Future of the Industry: AI and Automation
The wheel of development did not stop at inks and machines. Artificial Intelligence has begun to enter strongly into improving flag printing technologies.
-
Automated Defect Detection: High-resolution cameras monitor the printing process and detect any clogged print heads or color deviation and correct them instantly without human intervention.
-
Automated Laser Cutting: After printing, smart cutting tables equipped with cameras read registration marks and cut the flags, and even heat-seal the edges to prevent fraying, all in a matter of seconds.
Tips for Caring for Printed Flags
To maintain the quality of flags produced using the best flag printing technologies, a maintenance protocol must be followed:
-
Washing: It is preferable to wash sublimation-printed flags with lukewarm water and mild detergents.
-
Lowering: The flag must be lowered in case of winds exceeding 60 km/h, because the force of nature overcomes any technology.
-
Repair: Once a small tear is noticed at the free end of the flag, it must be stitched immediately to prevent the tear from expanding.
Conclusion
Investing in advanced flag printing technologies is not a luxury, but a necessity to ensure delivering the visual message in the best possible image. From dye sublimation that gives us vibrant colors, to digital printing that gives us speed, these solutions integrate to serve government sectors, companies, and individuals.
When you choose the right technology, the appropriate material, and the supplier who understands the complexities of color management, you do not just get a flag, but you get a moving piece of art that withstands time and remains standing tall in the sky.
 العربية
العربية
